Dear Aspirants, Our IBPS Guide team is providing new series of Reasoning Questions for IBPS RRB PO Mains 2019 so the aspirants can practice it on a daily basis. These questions are framed by our skilled experts after understanding your needs thoroughly. Aspirants can practice these new series questions daily to familiarize with the exact exam pattern and make your preparation effective.
Check here for IBPS RRB PO Mains Mock Test 2019
Check here for IBPS RRB Clerk Mains Mock Test 2019
Check here for IBPS PO Prelims Mock Test 2019
Click Here to Subscribe Crack High Level Puzzles & Seating Arrangement Questions PDF 2019 Plan
[WpProQuiz 7128]
Directions (1-4): Refer to the data below and answer the questions that follow. (2 Marks each)
P, Q, R, S, T, U, V and W are eight different people who have bought eight different cars – Honda, Mercedes, MG HECTOR, Tata, Tesla, Rolls Royce, Ford and Hyundai on eight different days starting from Monday to Monday. The cars are of eight different colours viz. Red, Blue, White, Yellow, Black, Grey, Beige and Silver. All the information is not necessarily in the same order.
Four people have bought the cars between Q and the person who has bought MG HECTOR. At least two people have bought cars after the person who has bought Ford. Grey and Red cars have not been bought immediately before or after a Yellow car. U has bought a car immediately after W. Hyundai is neither in Red nor in Silver colour. Neither P nor U has bought MG HECTOR. Beige car is bought 3 days before Mercedes was bought. S has bought a car either immediate or on one of the days after V but before the person who has bought Ford. Rolls Royce is neither in a Blue nor in a White colour. Only three people have bought cars between the person who has bought Honda and the person who has bought a yellow car. Only three people have bought cars between R and T. Tesla has been bought after Hyundai but neither immediately after nor on Monday. The Blue car is bought after the Black car. Q has bought a car on one of the days before the person who has bought MG HECTOR. The number of cars bought before Tesla is as same as the number of cars bought after Hyundai. Q has bought a Silver car. Only two people have bought the cars before S. T has not bought a car on the last day. P and S have not bought Mercedes nor Tata. Mercedes car is not in a Silver colour. Red car is bought immediately after Grey car but immediately before Black car.
1) Which of the following car is of White colour?
a) Honda
b) Mercedes
c) Hyundai
d) MG HECTOR
e) Ford
2) Which car has P bought?
a) Honda
b) Tata
c) Rolls Royce
d) Mercedes
e) MG HECTOR
3) W has bought car on which day?
a) Tuesday
b) Wednesday
c) Thursday
d) Friday
e) Saturday
4) Red coloured car was bought by whom?
a) P
b) W
c) S
d) Q
e) U
Directions (5-7): Refer to the data below and answer the questions that follow. (1 marks each)
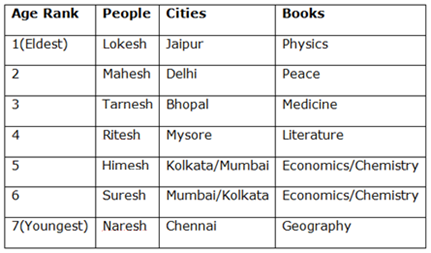
There are seven people Suresh, Mahesh, Ritesh, Himesh, Naresh, Lokesh and Tarnesh belong to 7 different Cities Jaipur, Delhi, Kolkata, Bhopal, Mumbai, Chennai and Mysore, but not necessarily in the same order. They also take interest in different types of books namely Physics, Chemistry, Economics, Medicine, Peace, Literature and Geography, not necessarily in the same order. Their liking towards certain books is dependent on age, such that the youngest person likes Geography while the eldest person likes Physics and in that order.
Only 1 person, who belongs to Chennai, is younger than Suresh. The one who prefers Literature, belong to Mysore. Only two people are elder than the one who belongs to Bhopal. Mahesh belongs to Delhi and is elder than the one who belongs to Bhopal. Ritesh is younger than the one who prefers Medicine but elder than the one who belongs Mumbai. A person who likes Physics belongs to Jaipur. Himesh is neither the youngest nor does he prefer Peace. Lokesh is elder than Himesh. Tarnesh is younger than Lokesh but is not the youngest one. The one who prefers Medicine is younger than one who prefers Peace. One of the people who is elder than Himesh belongs to Mysore.
5) How many people are younger than Ritesh?
a) One
b) Two
c) Four
d) Zero
e) None of these
6) Which of the following statement is true?
a) 2nd youngest person belong to Mumbai
b) 3rd youngest person belongs to Kolkata1
c) Suresh prefer Chemistry
d) Lokesh prefer Physics
e) All of the above
7) Who among the following is older than the person prefers Literature but younger than the person who belongs to Delhi?
a) Tarnesh
b) Ritesh
c) Himesh
d) Either Tarnesh or Ritesh
e) Either Himesh or Tarnesh
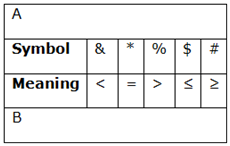
Direction (8-10): In the following question, the symbols &, *, %, $ and # are used with the following meaning as illustrated below.
‘A & B’ means ‘A is neither greater than nor equal to B’.
‘A * B’ means ‘A is neither greater than nor smaller than B’.
‘A % B’ means ‘A is neither smaller than nor equal to B’.
‘A $ B’ means ‘A is not greater than B’.
‘A # B’ means ‘A is not smaller than B’.
Now in each of the following questions assuming the given statements to be true, find which of the conclusion given below them is/are definitely true.
8) Statements:
P $ T, T * R, R # S, S % L
Conclusions:
I) R * P
II) R % P
III) L & T
IV) S $ T
a) Conclusions III, IV and either I or II are true.
b) Only conclusions II and III are true.
c) Only conclusions III and IV are true.
d) Either conclusion IV or III are true.
e) Only conclusions I and IV are true.
9) Statements:
K # L, L % M, M $ J
Conclusions:
I) J % L
II) M & K
III) M * K
a) Either conclusion I or II and III are true.
b) Only conclusion II is true.
c) Only conclusion III is true.
d) Either conclusion II or III is true.
e) Both conclusions I and III are true.
10) Statements:
Z # X, C % V, B & C, Z # V
Conclusions:
I) B & V
II) Z % C
III) V $ Z
IV) X & C
a) Conclusion III, IV and either I or II are true.
b) Only conclusion II is true.
c) Only conclusion III is true
d) Either conclusion IV or III is true.
e) Both conclusions I and IV are true.
Answers :
Directions (1-4):
1) Only two people have bought the cars before S.
2) Four people have bought the cars between Q and the person who has bought MG HECTOR.
3) Q has bought a car on one of the days before the person who has bought MG HECTOR.
4) Q has bought a Silver car.
5) The number of cars bought before Tesla is as same as the number of cars bought after Hyundai.
6) Hyundai is neither in Red nor in Silver colour.
7) Tesla has been bought after Hyundai but neither immediately nor on Monday.
Case 1
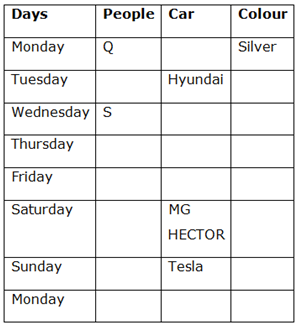
Case 2
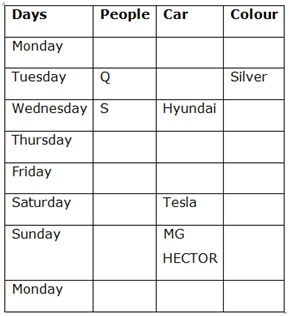
8) S has bought a car either immediate or on one of the days after V but before the person who has bought Ford.
9) At least two people have bought cars after the person who has bought Ford.
10) Only three people have bought cars between R and T.
11) T has not bought a car on the last day.
Case 1 (a)
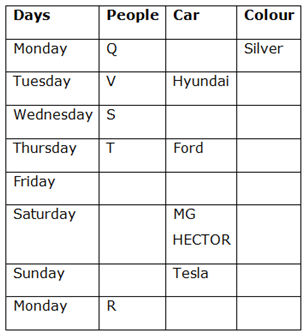
Case 1 (b)
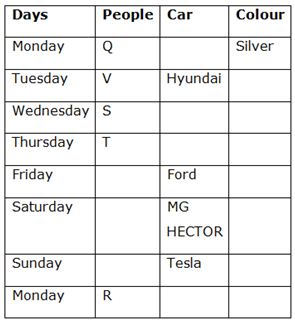
Case 2 (a)
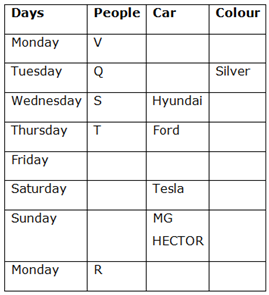
Case 2 (b)
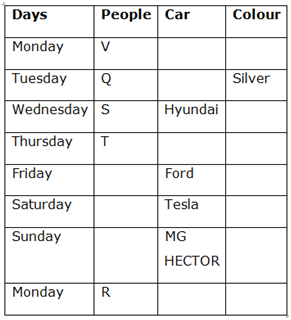
12) U has bought a car immediately after W.
13) Neither P nor U has bought MG HECTOR.
Thus, all three cases get eliminated except case 1 (a)
Case 1 (a)
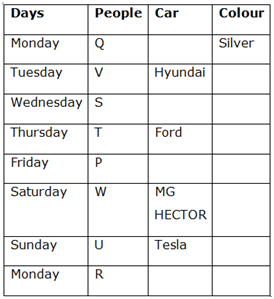
14) P and S have bought neither Mercedes nor Tata.
15) Mercedes car is not in a Silver colour.
So, R has bought Mercedes and Q has bought Tata.
Case 1 (a)
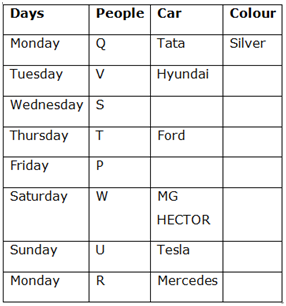
16) Only three people have bought cars between the person who has bought Honda and the person who has bought a yellow car.
17) Rolls Royce is neither in a Blue nor in a White colour.
18) Grey and Red cars have not been bought immediately before or after a Yellow car.
So, S has bought Honda and P has bought Rolls Royce.
Case 1 (a)
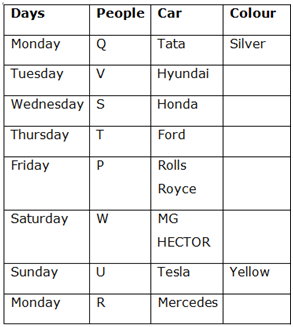
19) The Blue car is bought after the Black car.
20) Red car is bought immediately after Grey car but immediately before Black car.
21) Beige car is bought 3 days before Mercedes was bought.
Final Arrangement
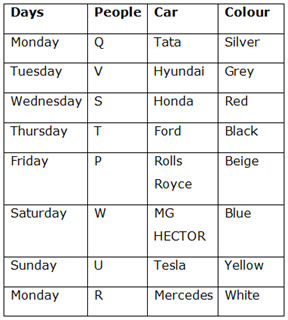
1) Answer: B
2) Answer: C
3) Answer: E
4) Answer: C
Directions (5-7):
1) Only 1 person who belongs to Chennai is younger than Suresh.
(Therefore Suresh will be 2nd youngest among them)
2) Only two people are elder than the one who belongs to Bhopal.
(Therefore, a person who belongs to Bhopal is 3rd oldest)
3) Mahesh belongs to Delhi and is elder than the one who belongs to Bhopal.
4) A person who likes physics belongs to Jaipur.
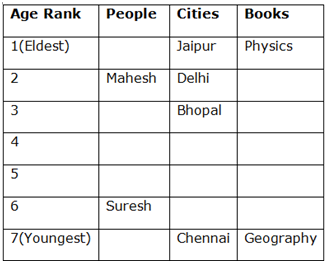
4) Tarnesh is younger than Lokesh but is not the youngest one
5) Lokesh is elder than Himesh.
6) Himesh is neither the youngest nor does he like Peace.
7) Ritesh is younger than the one who prefers Medicine but elder than the one who belongs to Mumbai.
(Therefore Ritesh also will not be the Youngest Person)
⇒ Tarnesh also will not be the youngest person as he elder Lokesh and Himesh.
Now the only person who is left is Naresh, therefore, Naresh is the youngest person.
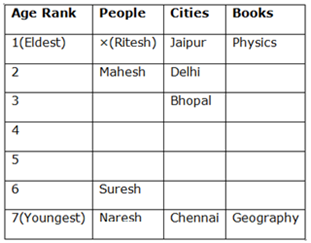
7) Ritesh is younger than the one who prefers Medicine but elder than the one who belongs Mumbai.
8) The one who prefers Literature belongs to Mysore.
9) The one who prefers Medicine is younger than one who prefers Peace.
10) A person who elder than Himesh belongs to Mysore.
5) Answer: E
6) Answer: D
7) Answer: A
8) Answer: A
According to the given information,
Given statement: P $ T, T * R, R # S, S % L
On converting: P ≤ T, T = R, R ≥ S, S > L
On combining: R = T ≥ P; R ≥ S > L
Conclusions:
I) R * P → R = P→ False (as R = T ≥ P → R ≥ P)
II) R % P → R > P→ False (as R = T ≥ P → R ≥ P)
III) L & T → L < T→ True (as R = T ≥ P; R ≥ S > L → T = R ≥ S > L → T > L)
IV) S $ T → S ≤ T→ True (as R = T ≥ P; R ≥ S > L → T = R ≥ S > L → T ≥ S)
Conclusions I and II are complementary pair.
Hence, either conclusion I or II follows.
Also, conclusion III and IV also follows.
9) Answer: B
According to the given information,
Given statement: K # L, L % M, M $ J
On converting: K ≥ L, L > M, M ≤ J
On combining: K ≥ L > M ≤ J
Conclusions:
I) J % L → J > L → False (as K ≥ L > M ≤ J, relation between J and L is not clear)
II) M & K → M < K → True (as K ≥ L > M → K > M)
III) M * K → M = K → False (as K ≥ L > M → K > M)
Hence, only conclusion II is true.
10) Answer: C
According to the given information,
Given statement: Z # X, C % V, B & C, Z # V
On converting: Z ≥ X, C > V, B < C, Z ≥ V
On combining: Z ≥ X, Z ≥ V, B < C > V
Conclusions:
I) B & V → B < V → False (as B < C > V, relation is not clear)
II) Z % C → Z > C → False (as Z ≥ V, B < C > V, relation is not clear)
III) V $ Z → V ≤ Z → True (as Z ≥ V)
IV) X & C → X < C → False (as Z ≥ X, Z ≥ V, B < C > V, relation is not clear)
Hence, only conclusion III is true.





